
Expressway
The Automatic Traffic Incident Detection System (ATID) provides all-weather, high-precision monitoring of various incidents on expressway segments. Front-end sensing devices report incident information in real time, using location coordinates, video images, and trajectory data to achieve lane-level accuracy in incident positioning. Incidents are quickly detected and addressed, with the entire process displayed to show the progress of incident handling, forming a closed-loop operational workflow. Through business data analysis, the system presents the operational status of the traffic network along with incident metrics, assisting users in decision-making.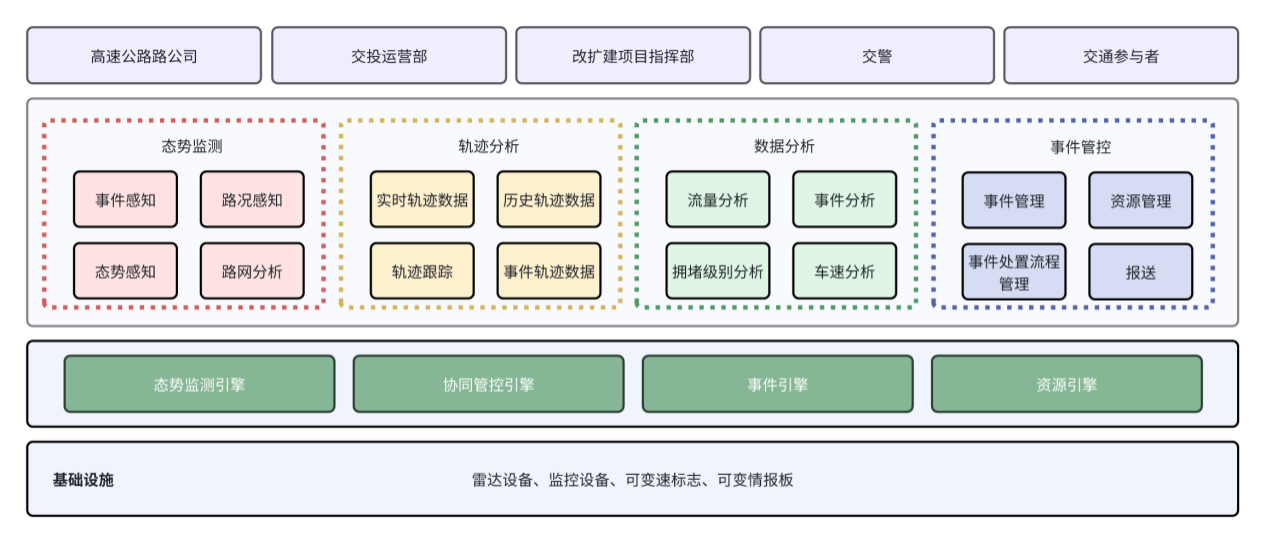
1. Radar-Camera Integration:
When an incident is reported, the system maps the event coordinates provided by the radar to the preset positions of the PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras. The cameras then automatically rotate to the nearest preset position to the incident location within a short time, achieving seamless coordination between radar and cameras.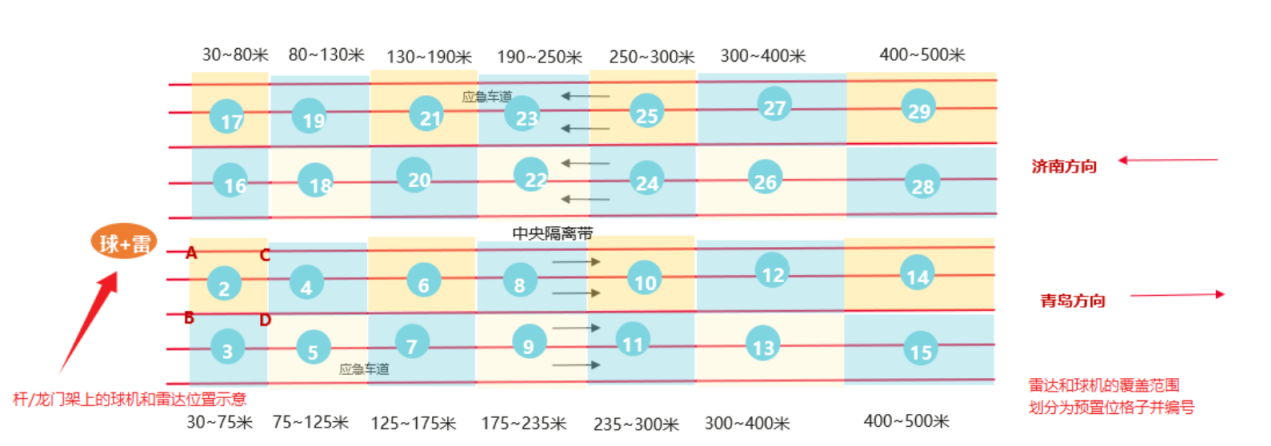
2. Event Fusion:
Using fusion algorithms, multiple independent but causally related events in the same direction are combined into a single fused event. The fused event can be processed in batches while reconstructing the causal sequence of the incident, reducing unnecessary repetitive work for users.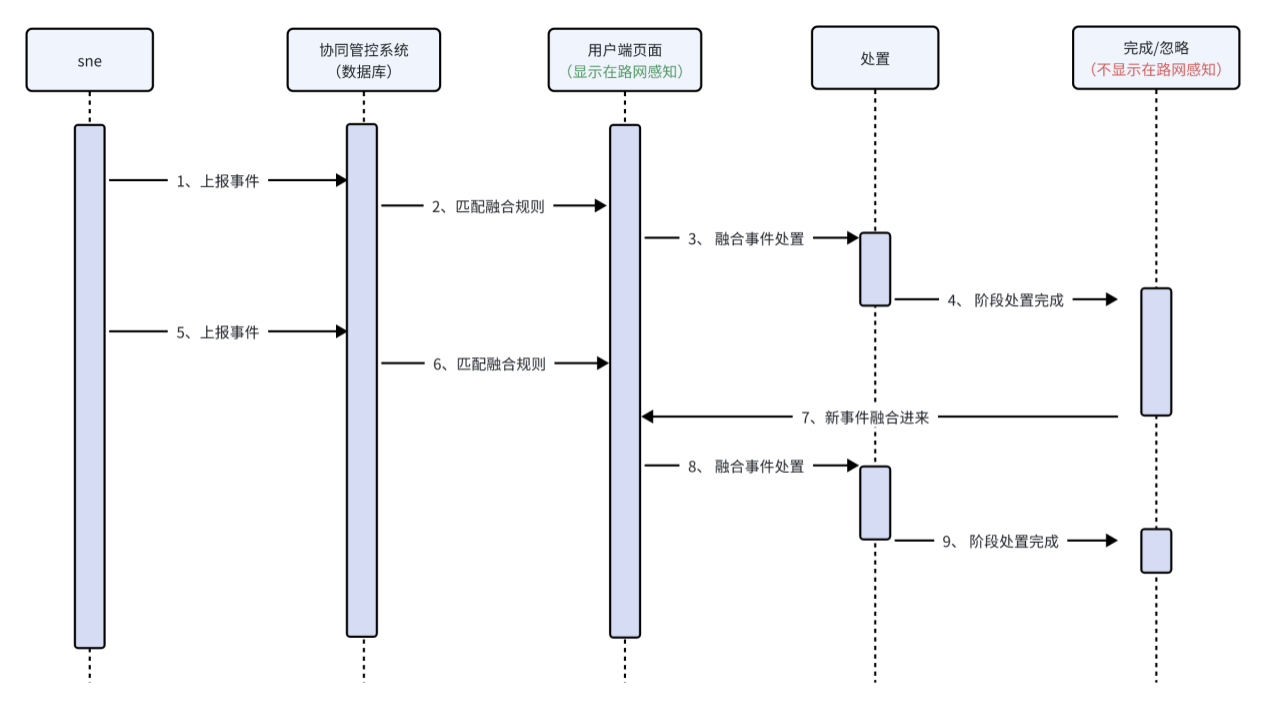
3. Closed-Loop Incident Handling Process:
Highway incidents are reported in real time, with the situation reconstructed through video trajectory analysis. An automatic evidence chain is generated, and preconfigured handling workflows are selected based on the incident information. When the incident is closed, video footage from the corresponding time period is recorded. The handling process is fully closed-loop, allowing the entire procedure to be tracked and reviewed.
4. Real-Time Vehicle Trajectory Monitoring: The historical vehicle trajectory restoration
system enables real-time tracking of the location, route, and driving patterns of vehicles in operation. For past vehicle movements, it can reconstruct the trajectories of accidents or special vehicles.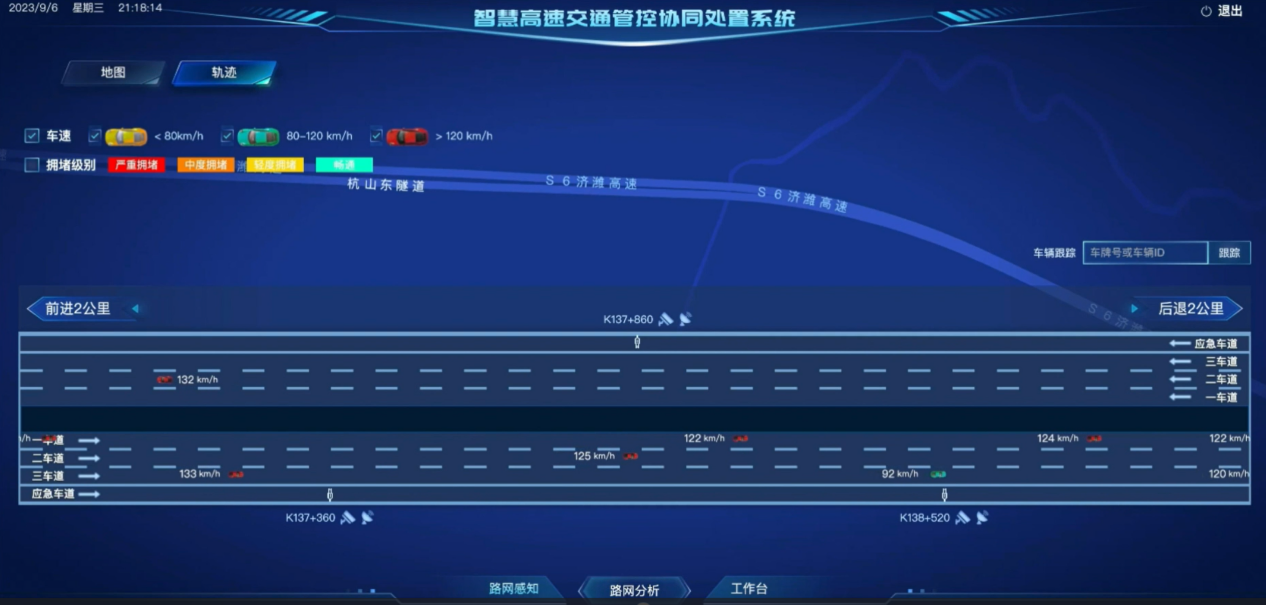
5. Geofencing for Event Filtering:
Users can manually define geofenced areas and create filtering rules. During the specified execution period, incidents occurring within these geofenced areas are automatically filtered.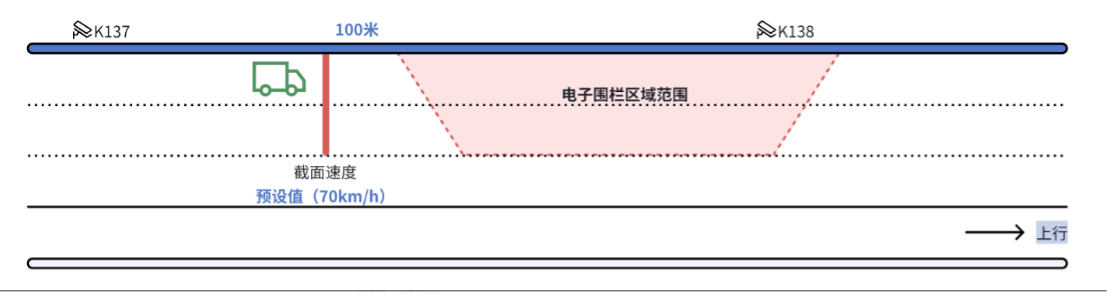
6. Algorithm-Based Safety Alerts:
The system provides safety warnings for scenarios such as suspected debris on the road or vehicles entering geofenced areas. The debris detection algorithm analyzes vehicle trajectory data, and when suspected debris is identified, a warning is displayed on the traffic network monitoring interface, prompting users to respond. For geofenced areas, speed thresholds can be set; if a vehicle exceeds the threshold, a warning appears on the traffic network monitoring interface.
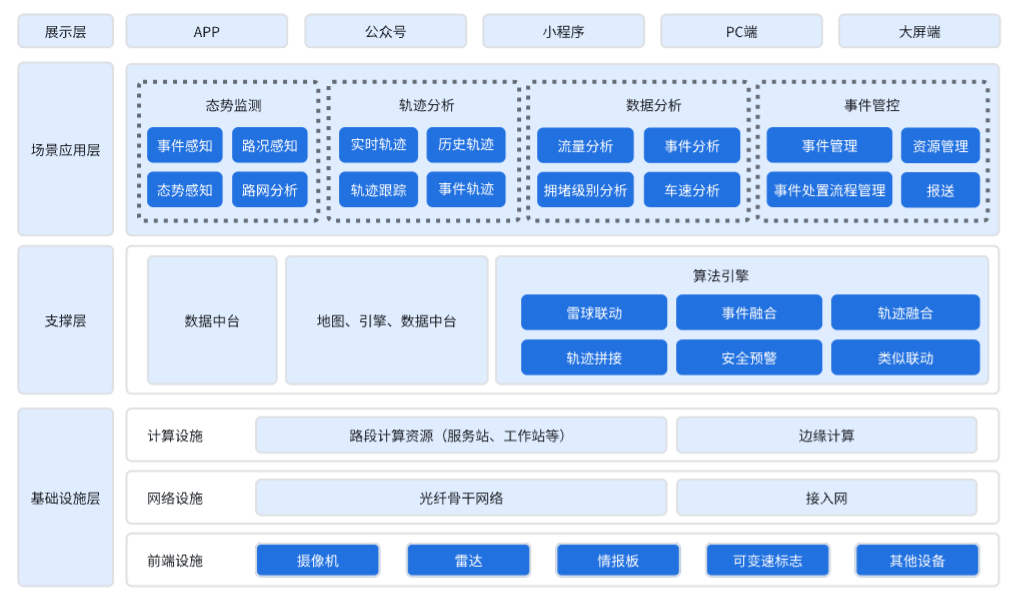
The overall system architecture consists of four layers: the Infrastructure Layer, the Support Layer, the Scenario Application Layer, and the Presentation Layer.
Infrastructure Layer: This layer primarily refers to the construction of foundational equipment that provides data support for upper-layer applications. It includes computing facilities, network facilities, and front-end facilities. Computing facilities comprise road segment computing resources such as servers and workstations, as well as edge computing devices. Network facilities include fiber optic networks and basic access network equipment. Front-end facilities include cameras, radars, and information boards.
Support Layer: This layer includes the group’s existing data platform and algorithm engines.
Scenario Application Layer: This layer refers to various systems built by leveraging the capabilities and algorithms provided by the Support Layer, tailored to different scenarios. It includes existing operational systems such as the integrated road-transport system, information board system, and video detection system.
Presentation Layer: The topmost layer of the data architecture, primarily used to display various aggregated data. It includes various scenarios, such as mobile apps, official accounts, mini-programs, PC interfaces, and large-screen displays.

1. Road Network Perception:
This function monitors expressway traffic conditions, roadway incidents, and trends in key indicators. Traditional road network management relies heavily on manual patrols, making it difficult to detect congestion, traffic accidents, or debris in real time. Road network monitoring, based on front-end sensing devices, ensures immediate detection of incidents such as accidents, congestion, and illegal parking, overcoming the limitations of manual inspections and vehicle patrols, and improving the efficiency of safety responses. Road network perception uses a map as the main interface, displaying incident and traffic information to provide a clear overview of road network operations.
2. Event Filtering:
This feature addresses situations such as road maintenance, large-scale traffic congestion, or long-duration congestion. Filtering conditions are set using event filtering rules or by defining geofenced areas. During the execution of these rules, incidents reported by front-end sensing devices are automatically filtered, and filtered events are not displayed on the road network perception interface.
3. Traffic Condition Status:
Based on vehicle trajectory data provided by sensing devices, the system analyzes and calculates traffic conditions, displaying the current congestion level and details for each road segment. Users can access information such as the congestion index, congestion level, congestion length, and start time for each road segment.
4. Roadside Devices:
Devices installed along the roadside, such as cameras, radars, information boards, and variable speed signs, allow users to view their locations and device information through the devices’ own functionalities.
5. Trajectory Applications:
This feature allows real-time monitoring of vehicle trajectory data, including vehicle speed and congestion levels for each road segment. The system can query, track, and locate special vehicles. Within the trajectory data retention period, users can specify a road segment range and time range to retrieve historical trajectory data, enabling tracking and localization of special vehicles in past data.
Scenario 1: Road Network Operation Monitoring
– This scenario performs analysis and visualization of indicators such as road congestion, vehicle speed, traffic flow, and incident data, enabling users to intuitively understand the overall traffic situation and key metrics. It transforms traditional paper-based incident records into digital, visualized, and dynamic data.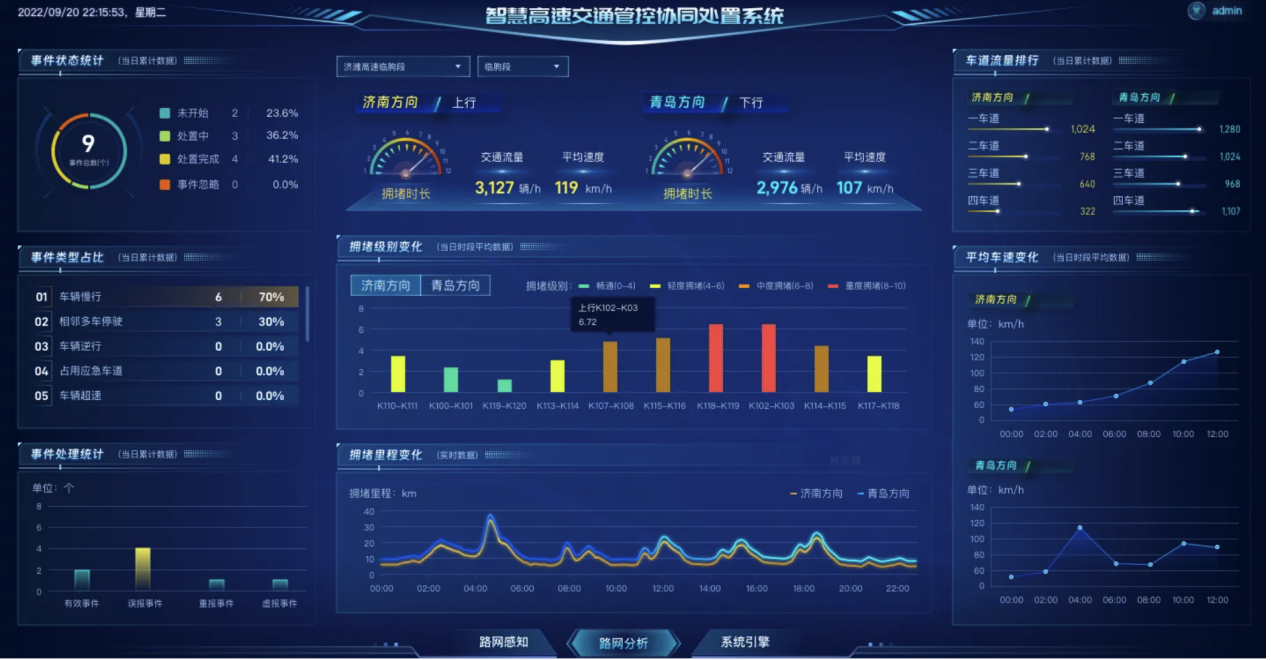
Scenario 2: Expressway Traffic Incident Detection and Handling
– This scenario monitors expressway traffic conditions, roadway incidents, and trends in key indicators. Traditional road network management relies heavily on manual patrols, making it difficult to detect congestion, traffic accidents, or debris in real time. Road network monitoring, based on front-end sensing devices, ensures immediate detection of incidents such as accidents, congestion, and illegal parking, overcoming the limitations of manual inspections and vehicle patrols, and improving the efficiency of safety responses.

Suqian Smart Expressway Collaborative Management and Control Platform